Chemical reactions happen continually around you. Two important types of chemical reactions are combustion and corrosion. Combustion happens when anything burns or explodes. Corrosion happens when a metal such as copper or an alloy such as steel changes into something else. Similar substances tend to undergo similar chemical reactions. These similarities allow you to produce what might happen if two chemicals are mixed. The similarities become more obvious when chemical reactions are expressed as chemical equation.
Endothermic and exothermic reactions
- Reactants are the substances you started with before the chemical reaction.
- Products are substances that are formed by chemical reactions.
- Reactions can or release energy (get hot) these are exothermic.
- Reactions can absorb energy (get cold) these are endothermic
Combustion
Combustion reactions are examples of exothermic reaction. combustion occurs whenever something reacts with oxygen gas (O2), burning or exploding as it does so. A bushfire is a series of combustion reactions.
A bushfire is a series of combustion reactions. The chemical in living plants and dead twigs and leaves burn in oxygen, releasing huge amounts of heat and light as they react.



Combustion of fossil fuels
Bunsen burners, gas stoves, water heaters, and central heating furnaces produce a hot blue flame by burning methane or ethane gas in oxygen.
The reactions are:

Petrol is a mixture of highly combustible chemicals called hydrocarbons, the most important of which is octane. Octane combusts via the chemical equation:
![]()
Incomplete combustion
- When combustion reactions have enough oxygen it is known as complete combustion
- When combustion reactions do not have enough oxygen known as incomplete combustion
- Incomplete combustion does not release as much heat or light energy as complete combustion does.
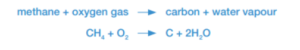
The reactions below show what happens to methane if oxygen is restricted.
![]()
At the same time, another reaction occurs
A Bunsen burner can show both complete and incomplete combustion. If the flow of oxygen to it is good (open-air hole), then the flame is hot, clean, and blue. If the airflow is restricted (close airhole), then a cooler, dirty yellow flame is produced.
Pollution and climate change
Water vapor and carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere whenever fossil fuels such as gas, petrol, oil, coal, diesel, and aviation fuel are burnt. Humans have burned huge quantities of fossil fuels to power their cars, ships, and aircraft and heat their homes, and generate electricity. For this reason, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased to levels that most scientists agree are increasing the atmosphere’s average temperature.
Carbon adds relatively harmless but dirty soot to the atmosphere. Carbon monoxide gas has no smell, but it is so poisonous that even small amounts of it can kill. Petrol also contains additives that release other poisonous chemicals when burnt. These include oxides of nitrogen and sulfur, both of which can combine with moisture in the air to form smog and acid rain.
Other combustion reactions
Our bodies have a much slower and more controlled combustion reaction that occurs within the cells of our body. Aerobic respiration combines the sugar glucose from the digestion of your food with the oxygen you breathe in. This reaction releases the energy that cells of your body need. We produce carbon dioxide as a waste product.
![]()
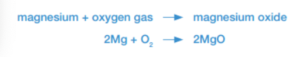
Not all combustion reactions produce carbon dioxide and water vapor. When burnt, magnesium reacts to form magnesium oxide.
Corrosion reactions
- Corrosion s a chemical reaction that forms other compounds from these metals.
- Eg. The iron/steel body of a car slowly reacts with water and oxygen in the air and will corrode until all that is left is a pile of rust.
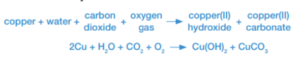
In a similar way, copper corrodes by reacting with gases in the air to form a green verdigris, a mixture of copper(II) hydroxide and copper (II) carbonate.

Pure silver reacts with sulfur to form a black coating called tarnish silver sulfide.
This sulfur comes from hydrogen sulfide in air pollution or from foods such as eggs, fish, onions, and pea soup.
![]()
Pure sodium and potassium are such reactive metals that they react with just about anything. Their corrosion is very quick and often explosive because of the hydrogen gas that their reaction produces. Their chemical reaction with water are sown below:

Rusting
Iron and its alloy, steel, are common and relatively cheap, making them the most commonly used metals on Earth. Most types of iron react with water to form rust also known as iron oxide.

Corrosion of aluminum
Aluminum is very reactive. The surface metal reacts almost immediately with the air, forming a fine layer of dull, grey aluminum oxide (Al2O3)

Unlike rust, this layer acts as a tightly bound layer of paint, protecting the aluminum from further corrosion.
Anodising is a process that deliberately builds up a layer of aluminum oxide to protect the aluminum underneath.



