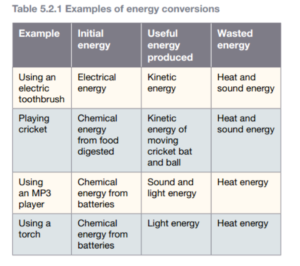
Useful and wasted energy
Any objects that moves, or has moving parts, has kinetic energy. A child pushing a toy car gives the car kinetic energy. When the child stops pushing the car comes to a standstill. This is because of the friction caused by the wheels and the carpet, which leads to heat, which is wasted energy.
In a similar way, a light bulb, quickly gets hot, releasing heat energy. This is wasted energy because you don’t use a light bulb for its heat.

Most energy conversations waste some energy. This is known as ‘wasted’ energy which usually comes in the form of heat and sound.
Energy efficiency
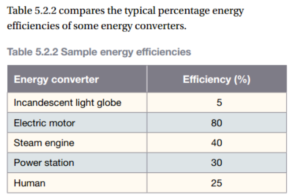
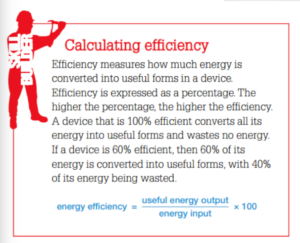
Energy efficiency is a measure of how much input energy is converted into useful output energy. The greater the proportion of useful output energy, the greater the energy efficiency of the device.
- If most of the input energy is converted into useful out put then the device is energy efficient.
- If a lot of the input energy is wasted, then the device is inefficient.

Renewable and non-renewable energy
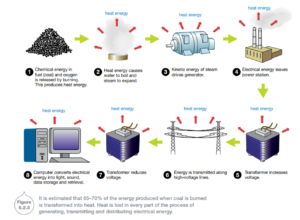
Some energy sources are renewable. This means that they are unlimited in supply and can be used over and over again. Examples are solar energy, wind energy, and hydroelectric energy. Most of the electrical energy that supplies Australian households comes from burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil or natural gas.
Fossil fuels were formed over millions of yearsa and are known as non-renewable energy source. Fossil fuels contain chemical potential energy, which is released when the fuel is burnt. Over 10 million tonnes of coal is burned each year to meet the electrical energy demand across New South Wales.
Reducing energy consumption
As the quality of life increases for people around the world. The demand for energy has never been greater than it is today. Most of the energy that we rely on to power our cars, heat and cool our homes and run electronic devices is produced from non-renewable sources, such as coal, natural gas and oil. These non-renewable energy sources are limited in supply and burning them adds greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. More and more people are realizing that these greenhouse gases increase the risk of global warming and that may cause climate change.
In Australia, climate change is likely to:
- cause more frequent and intense droughts, storms and floods
- Assist the spread of diseases, especially mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue fever and Ross River virus
- alter the population of different species of plants and animals, especially those that live above the snowline in the southern states
- raise sea levels, putting some coastal areas, towns and suburbs at risk of flooding.
Reducing the amount of energy we use reduces the amount of greenhouse gases put into the atmosphere. We can reduce energy consumption in many ways, such as switching off lights, computers and televisions when they are not in use. Walking, cycling or using public transport instead of relying on the family car will reduce your household’s energy consumption.
Energy rating labels
Household appliances vary in their energy efficiency.

Energy efficiency is shown by the number of stars on the label. The more stars (usually from 1 to 10) that are shaded on the energy rating label, the greater the energy efficiency of the appliance.
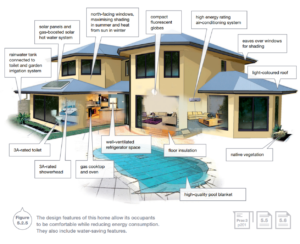
Efficient housing
Living in an energy-efficient house makes it easier for households to reduce their energy consumption. It is estimated that bout half of the enrgty costs of running a house are to keep it warm in winter and cool in summer. Heat naturally flows fom regions of higher temperature to regions of lower temperature. In winter, the warm air from a heater or heating system can flow through any cracks or gaps in the walls to the cool air outside or into the cooler garage.
Alternatively, heat can rise up into the roof space. this means that a lot of energy is needed to keep a leaky house warm in winter. Similarly, in summer, the warm air outside will naturally flow into a cool house.
To keep the house cool, air-conditioning might be used. However they use a lot of energy, making them expensive to run. Adding insulation to ceilings and between the walls of a home reduces the heat flowing outside in winter and inside in summer. This makes heating and cooling more effective and mask a house more comfortable.
Several improvements can be made to house designs to improve insulation:
- Considering the orientation of windows- In Australia, this means placing large windows along the northern and eastern sides of the house, with small or no windows on the hot western and the cooler southern side.
- Considering the orientation of the house on the block of land- In Australia, this usually means having living areas facing norht and other rooms (such as the bathrooms) facing south
- tinting or shading west-facing windows
- including coverings such as eaves, verandas or pergolas over the north and west facing windows
- insulating the floor, walls and roof to reduce energy loses
Innovative design
The need to save energy has led to a new and innovative designs to increase efficiency. Some of these ideas include regenerative braking, interior cooling in parked cars, magnetic refrigeration, LED lighting and much more.
The regenerative braking systems of a hybrid car captures some of the vehicle’s kinetic energy as the car slows down. Stored in a battery, this energy is then used to power the car’s electric motor when needed.
Organic photovoltaic are a new generation of flexible and cheap solar cells that are made from carbon-based materials. Researchers are trying to increase the efficiency of a traditional photovoltaic cell. If their efficiency can be improved, these cells have huge potential for widespread use. An organic photovoltaic cell is shown below.





