The human reproductive system enable us to produce offspring. It also affects how humans function as an organism. Chemicals from your reproductive organs affect your behaviour, the way you grow, your appearance and how your body works.
The female reproductive system has the role of producing a baby.
The eggs, or ova, are produced in the Ovaries. The ovaries are similar in size to an olive. They usually only release only one ovum (a single egg) each month, alternating between left and right ovaries. The egg forms in a capsule called a follicle. The egg then bursts out of the follicle.

The fallopian tubes, or oviducts, are tubes down which the egg passes on its way to the uterus. If the egg meets a sperm and becomes fertilized, then it is usually in this tube.
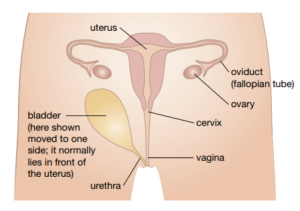
The uterus (or womb) is a thick-walled muscular organ that is about 7cm long and 5cm wide. It has a lining that can change and become rich in bloods vessels. A fertilised egg burrows into this lining. The baby grows and develops in the uterus until birth. The Uterus can swell up to many times its normal size to allow the baby room to grow. If the egg was not fertilised, then it passes out of the uterus through the lower end.
At the lower part of the uterus is a ring of muscle called the cervix. The cervix has the job of contracting tightly to hold the uterus closed while the baby is developing. This protects the baby in the womb. The cervix opens up when the baby is about to be born.
The vagina is where the male penis is inserted to deposit the sperm inside the female body. it is also the birth canal down which the baby passes.
The menstrual cycle
Reproduction in males and females is controlled by chemicals called hormones that are produced in the body and travel around in the bloodstream. One female hormone (known as FSH) causes the follicle to mature. Another hormone makes the egg burst out of the follicle. This is called ovulation.
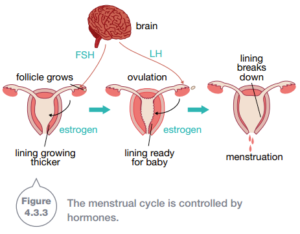
If the egg is not fertilized and implanted, the thickened lining of the uterus breaks down. Over the next few days some blood, along with much of the lining of the uterus passes out of the body. The events are menstruation commonly known as a period.


The male reproductive system
The role of the male reproductive system is to produce and deliver sperm.
Sperm are produced in the testes. There are two tests, which are also known as testicles. A single testicle is called a testis. The testicle hangs outside the body in a sac called the scrotum.
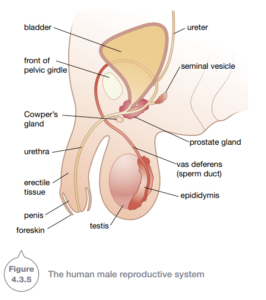
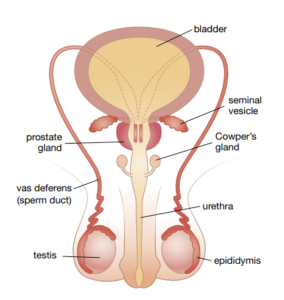
Sperm are killed or deformed if they become too hot. It is cooler in the scrotum than inside the body, which helps to prevent the sperm being killed or deformed. Millions of sperm are produced in tubes inside the testes. Then they are squeezed into a coiled tube called the epididymis. There is one epididymis on the outside of each testis. Sperm mature inside the epididymis.
To get to the outside of the body, sperm are squeezed by muscles lining the epididymis. They are pushed into a hallow tube about 45 cm long called the sperm duct, or vas deferens. This tube has muscles in its walls that squeeze the sperm along. On the way, fluid is added to the sperm from glands called seminal vesicles. This fluid contains various chemicals such as sugars that provide an energy source for the sperm.
There is also fluid added to the sperm by the prostate gland and Cowper’s glands. This mixture of sperm and other fluid is called semen. semen passes out of the penis through the urethra, the same tube through which urine flows. Urine cannot pass through at the same time as semen.
Puberty
Puberty is the time in a person’s life when they become sexually mature and able to reproduce. The physical changes of puberty take several years to complete. For boys, puberty is when fertile sperm are able to be produced. For girls, it is when the first ovulation occurs.
The time in the life cycle when puberty begins varies greatly. In Australia, girls begin puberty around 12 years of age on average, while boys are generally about 13. However, every person’s body is different- you reach puberty when your body is ready.
Changes in males
The early changes of puberty in males are increased levels of some homones such as testerone. These lead to changes, such as:
- Enlargement of the testes
- sperm formation by the testes
- growth of the penis
- The voice ‘breaking’ to become deeper
- hair growth on the face, arms, chest and groin
- increased muscle and bone growth and strength
- sudden increase in height and chest capacity
Changes in females
In girls, the early changes are increased levels of hormones such as Follicle Stimulated Hormone (FSH) and LH. These hormones cause an increase in estrogen. These hormonal changes result in changes such as:
- The breasts begin to enlarge (generally the first sign of puberty)
- Hair growth on the armpits and groin
- a sudden growth spurt
- the first period
- widening of the hips
- more fat deposited in the hips


