Gravity
- Gravity is the pulling force that makes you fall off your skateboard or chair.
- Gravity is a non-contact force
- Around every mass, there is something known as a gravitational field that attracts other masses. This attractive force is gravity, and it attempts to pull masses together.
- The greater the mass the greater the gravity of an object. This means that it is better at attracting other masses nearby.
- The gravity of smaller objects such as a pencil is so small that you hardly notice them.
- Gravity is only noticeable when one of the objects is really massive, eg. a planet, moon, or star
- Distance affects the gravitational fields, the further away something is from an object the less gravity that thing experiences from the object.

Orbits
The gravitational fields of massive objects like planets, moons, and stars trap other mass. Earth and the other planets of the solar system are ‘trapped’ by the gravitational field of the Sun and so they orbit it.
In the same way, the moon orbits the earth.
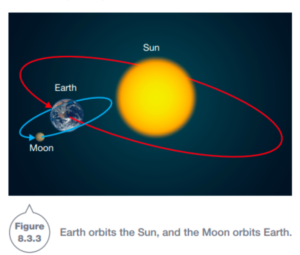

Objects that are in orbits like this are known as Satellites. The planets of the solar system are natural satellites of the sun, and the Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth.
Earth also has many man-made satellites.

Orbits in the solar system
- The orbits in the solar system are ellipses (oval-shaped)

The moon’s orbit
- The moon’s orbit is approximately 30 days.
- The orbit of the moon around Earth is nearly circular and constantly changes slightly.
- When the moon blocks the sun it is known as an eclipse.
Solar eclipses
- A solar eclipse occurs whenever light from the Sun is blocked by the Moon, casting a shadow onto Earth.
- Solar eclipses can be complete (in the umbra, where the shadow is full and dark) or partial (in the penumbra, where the shadow is dark and dense).


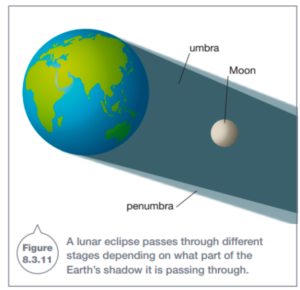
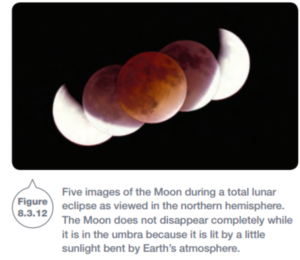
Lunar Eclipses
- During a lunar eclipse, the earth blocks light from reaching the Moon.
- The earth casts a shadow on the moon.
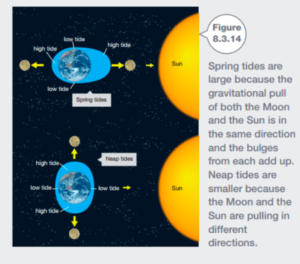
Tides
- The gravitational pull of the moon drags all the water in the oceans and seas towards it, causing a bulge on the side of the Earth that faces the moon.
- On the opposite side of the Earth, the Moons Gravitational pull is weaker and causes there to be a bulge on the other side of the moon facing away from the earth.