Some living things prefer to live in a hot dry environments such as the deserts of inland Australia. Others prefer wetlands, rain forests or coral reefs.
Habitats
All organisms (living things) have a place where they live. This is called their habitat.
Every living thing has particular needs, and will live only where these needs are met by the resources available in the habitat. Some of the resources a habitat must provide for an organism to survive and reproduce include:
- food
- water
- shelter and living space
- a suitable temperature
- mating partners for reproduction
- gases such as oxygen

Biotic and Abiotic factors
- Biotic factors- These are living factors that include partners for mating, organisms to eat, and organisms they may compete with for food and shelter.
- Abiotic factors- These are non-living factors that include light, wind, soil, air and temperature.
Adaptations
To survive in their habitat, organisms have adaptations. Adaptations are characteristics that assist organisms in surviving and reproducing. Adaptations help organisms to get food and water, protect themselves, build homes and reproduce.
The position of the eyes and nostrils of a crocodile are adaptations. They allow the crocodile to breathe air and look for prey when the crocodile is almost totally submerged in the water.
The spotted-tail quail is a marsupial that lives in eastern Australia’s wet and dry forests, from Queensland through NSW to Tasmania. The quail’s coloring means that it is well camouflaged. This allows it to sleep in hollow trees and rock crevices without being seen by other animals that would hunt it for food. A quail uses its sharp claws and teeth to catch rats, birds and reptiles but will also eat dead remains. Qualls are nocturnal, which means they are active and hunt at night. A quail can see in dim light.

Native trees growing in parts of Australia need to survive frequent fires. Some trees like eucalyptus (gum trees) have buds buried deep within the trunk where they are protected from the heat of the fire. Normally these buds do not sprout. However, if a fire destroys most of the leaves on the tree, these buds grow and quickly cover the tree with new leaves.

All plants need light if they are to survive. Plants use the energy from sunlight to help them make their food. Plants growing in dense rainforests often have adaptations such as hooks on stems and leaves, or long, thin threads called tendrils to help them climb over other plants to reach the sunlight. Smilax (shown in Figure 5.1.5) is a common plant in Australian forests.
It sends out tendrils that coil around neighboring branches.

Adaptations enable animals to:
- Protect themselves from predators (camouflage)
- Survive hot and cold temperatures, and wet and dry seasons
- move from place to place (flippers, legs, and wings)
- catch and eat food
- Take in oxygen
- Reproduce
Adaptations enable plants to:
- protect themselves from grazing animals (toxins, spines, and thorns)
- take oxygen and carbon dioxide
- take in water (very long roots)
- Capture light (large leaves)
- reproduce
Where organisms live
Some organisms can live almost anywhere. they are able to find suitable habitats in a wide range of areas.
For example, the red kangaroo shown in Figure 5.1.6 can be found in arid and semi-arid regions from the extreme north of the east coast to the southwest of mainland Australia.


Other organisms live in very restricted areas. The mountain pygmy-possum is a threatened Australian marsupial. It is adapted to habitats found only in mountains at a height of over 1400 meters. Figure 5.1.7 shows the extent of the habitat in which the mountain pygmy-possum is found.


Environmental conditions
How well an organism survives depends on how well it is adapted to the environmental conditions in the area.
Many biotic and abiotic factors that may shape and change an environment include:
- the temperature
- whether it is wet or dry
- whether it is windy
- the quality of the air
- the water quality
- the type of soil
- the plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi that live there.
Ecologists are scientists who study interactions between living things.
Living together
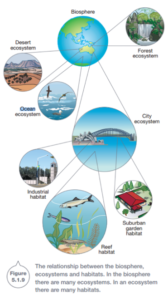
The biosphere is the place where all life as we know it exists.
An ecosystem is a system formed by organisms interacting with each other and their nonliving surroundings in a balanced way.
Environmental conditions
How well an organism survives depends on how well it is adapted to the environmental conditions in the area.
Many biotic and abiotic factors that may shape and change an environment include:
- the temperature
- whether it is wet or dry
- whether it is windy
- the quality of the air
- the water quality
- the type of soil
- the plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi that live there.
Ecologists are scientists who study interactions between living things.
Living together
The biosphere is the place where all life as we know it exists.
An ecosystem is a system formed by organisms interacting with each other and their nonliving surroundings in a balanced way.
The organisms in an ecosystem are interdependent.
Interdependent organisms depend on each other for survival.
There are three main types of interdependence or symbiosis.
- Commensalism- One organism benefits and the other is unaffected.
- Mutualism- both organisms benefit
- Parasitism- one organism benefits, the other is harmed



