Water as a solvent

Water is vital for life. Drought in much of Australia has forced us to conserve water and explore new ways of obtaining water to drink, cook and shower in. Traditionally water has come from rivers and dams, but increasingly we are turning to groundwater (water found underwater) and new technologies such as desalination to provide us with a reliable supply.
Is water pure or a mixture?
Most of the time, water is a mixture of many substances, why? lets look at some common examples of ‘water’.
- lakes- contain water, and tiny organisms, salts, fertilizers
- swimming pools- containing water, and chlorine
- rain- contains water, but as it falls it collects dust
- sea water-contains water, but a LOT of salt and tiny organisms, fish and waste
- Freshwater in rivers- contains water, and dissolved oxygen (fish breath this in)
So most water in the world exists as a mixture.
Fun fact: of the world’s water, 98% is salt water in the oceans. Of the world’s fresh water, 77% is ice. So only 23% of the worlds fresh water is shared between human drinking water, lakes, rivers and dams.
water and life
- All organisms NEED WATER, without it all living things die.
- All organisms are made of cells and need to dissolve the nutrients inside their bodies allows these chemicals to move around and keeps us alive
- Without water these nutrients won’t move around, and so organisms will die.
Water in daily life
Water is used in daily life for the following:
- Dissolves soap and detergent to help you to wash yourself shampoo your hair and to wash clothes, dishes and cars.
- It dissolves sugars and food coloring’s in soft drinks and fruit juices.
- Water is used in cooking
- Water helps to keep plants in the garden alive
Water is used in many aspects of industry.
We know that water is a solvent, because of this we see it used in many industries such as in:
- Medical industry
- Agriculture
- Fertilizer
- Pesticides
- Mining industry
- Manufacturing

Water and the environment
Water has the following functions in the environment:
- it dissolves minerals such as calcium, iron, phosphate, potassium and zinc
- This allows plants to absorb them through their roots
- These minerals can be passed onto animals that eat them
Water sources
There are 3 main sources of freshwater water:
- Rivers
- Dams and lakes
- Groundwater
Water treatment
Water that is fit to drink is called potable water. While water is unfit to drink is known as non-potable water.
In order to make water fit to drink, it needs to be sent to a treatment plant before it is supplied as potable water to homes and businesses.
The 5 stages of water treatment are:
- Flocculation– solid particles are separated using chemicals known as flocculants which make them clump together and then easily skimmed off the surface or drop to the bottom and the water is drained off the top.
- Filtration– The water is pumped through filters.
- Sterilization- adding chlorine to kill bacteria
- Balancing pH- making sure it is not acidic or basic
- Fluoridation- Fluoride, a chemical also found in your toothpaste, is added to reduce the chance of tooth decay.
Sydney has one of the best water in the world. Here’s how we treat our drinking water.
Some places in the world have little fresh water in the form of lakes and rivers. Places like the middle east desperately need fresh water for their citizens.
Desalination can be used to remove the salt from sea water and make it drinkable.
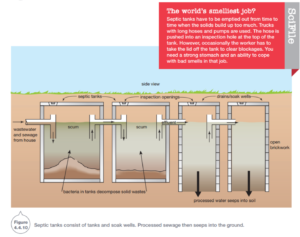
Sewage
Sewage is waster water from places like kitchens, bathrooms, toilets and laundries.
In australia there are 2 ways to remove and process sewage:
The sewage system– this is a system of underground pipes that carry the sewage into a waste treatment plant. Once the water is safe again it can be pumped to the ocean or used to irrigate crops and vegetable gardens.
Septic tanks- these tanks process the sewage from houses na businesses located beyond the sewage from houses and businesses located beyond the sewage system. The water soaks through several layers and tanks of filtration material and the clean water drips down into the groundwater.