Burning coal generates most of our electricity. Fossil fuels produce vast amounts of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide. This makes Australia one of the highest rates of greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Renewable resources such as wind, solar, tidal, hydroelectricity and biomass provide sustainable and clean alternatives.
Modern humans have very high energy demands. Appliances and gadgets, such as televisions, mobile phones, home entertainment units, gaming consoles and computers, requires a lot of energy to manufacture.

Non-renewable energy
Oil, coal, gas an nuclear are energy sources that cannot be replaced. Energy sources such as these are called non-renewable energy sources.
Oil, coal, gas and their products are known as fossil fuels. Some 300 millions years ago, the dead remains of prehistoric animals and plants were converted by layers of mud, sand and dirt. When burnt, fossil fuels release large amounts of energy but also large amounts of the green house gas carbon dioxide. This increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is thought to contribute to climate change.
Nuclear fuels, such as uranium and plutonium, and non-renewable sources of energy that are used as the main power source in many countries overseas.
The major energy sources used in Australia include:
- Black and brown coal, to produce steam used to generate most of our electricity
- Petrol to power most of our cars, with some using liquid petroleum another fossil fuel
- Diesel to power most trucks, cars and tractors and some trains
- natural gas for much of our cooking, central heating and hot water services
Renewable energy sources
Renewable energy sources can be used over and over again. If we want to build an energy supply for the future and to limit greenhouse gas emissions then we need to switch from fossil fuels to renewable sources.
Key sources of renewable energy are:
- moving water
- heat within the earth
- Sun
- wind
- oceans and rivers
- biomass

Hydroelectricity
Gravity causes things to fall, including water. Water falling from a higher to a lower level, such as from the dam can be used to turn turbines and generate electricity.
This form of electricity is called hydroelectricity.

Biomass
Biomass is material, such as dead plants, other types of plant matter, or animals and their wastes, from which energy can be obtaiend. These materials contain stored energy captured from the Sun. This energy can be released from use in many different ways:
- Heat energy is released when products such as wood, peat or dried manure, such as cow pats, are burnt
- When organic wastes such as fruit peelings and grass clippings are put into landfill, producing methane and carbon dioxide gas. This is called biogas and can be used as fuels.
- Biofuels is liquid fuel made from living things like plants or algae. For example, ethanol can be fermented from agricultural crops, such as sugarcane or corn.

Solar energy
Light from the sun is a valuable renewable resource. It can be used in many ways to provide energy.
- The direction a house faces can help reduce the need for additional heating and cooling. Using interior materials that absorb sunlight through the day and then release heat at night also helps
- Sunlight can be used to heat water flowing through rooftop solar collectors to provide households with hot water
- Solar cells use materials called semiconductors to convert sunlight directly into electricity. Rooftop solar cells can provide household electricity, and any extra electricity generated can be fed back into the electricity grid or into storage batteries. Solar cells are expensive to produce, but the amount of electricity they make it increasing each year. this increased efficiency of solar cells is making them more affordable to households.
- A solar pond consists of a large volume of water to which salt is added. The pond is lined with black plastic. Sunlight heats water at the base of the pond, and the heat can be used to generate electricity
- Large- scale solar energy systems, rely upon vast arrays of mirrors to concentrate sunlight. These devices can be used to generate electricity with no greenhouse gas emissions.

Wind energy
Wind energy has been used for centuries and windmills have long been used in Australia to pump water. Wind turbines are like large windmills but are used to generate electricity. Wind farms are located in windy places.

Energy from the ocean
There are a number of different techniques that harness energy from the ocean. Although these techniques are generally expensive to establish, they offer a clean energy source once they offer a clean energy source once they are operating. An oscillating wave column and a tidal barrage.


Geothermal energy
Beneath the Earth’s crust lies molten magma. Ice land, Japan and New Zealand, this heat lies fairly close to the surface and heated water may burst from the surface as a natural hot springs.
This heated water can be used directly to generate electricity. Another way to use geothermal energy is to pump water underground through drilled channels and circulate it through the hot rock. The water is heated by the rock and is used to generate electricity when it returns to the surface. Geothermal power plants are being developed in South Australia. Geothermal power plants tap into a plentiful natural energy source. However, they are limited to specific areas and can result in pollutant gases escaping from below Earth’s surface.

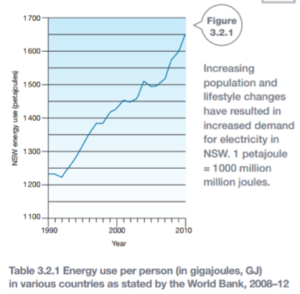
Powering NSW
Fossil fuels supply 94% of the energy needed in NSW. Coal and petroleum (petrol) make up most of the fossil fuels used. Electricity supplied by renewable sources is a small part of the total energy used in the state.
Electricity generated from renewable sources is on the rise. From 2001-2008, electricity from renewable sources contributed 6% of the total electricity produced but by 2010 this type of energy supply had doubled. In NSW, the main renewables used are hydroelectricity, biomass (wood, wood waste, bio gas, bio fuels) and, increasingly, wind and solar energy.

The coal mining industry provides a reliable source of energy, income and employment, but there are serious concerns about its impact on the environment. These include:
- The emission or large quantities of greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide) produced when coal is burnt
- pollution of surface and groundwater
- erosion and changes to the land form
- changes to the environment that might make it more difficult for different types animals and plants to survive
Carbon capture and storage is the process whereby carbon dioxide gas is isolated and captured either before or after coal is burnt. Once captured, the carbon dioxide is liquified.
Nuclear Energy



