Natural and Made Resources
Humans require many things to live, such as food, air, water, and shelter. These needs are met by the natural resources of the earth. We are all responsible for protecting the vital resources found on earth.
Natural Resources
A resource is anything obtained from the Earth to satisfy a particular need of humans or other living things. Most natural resources include rocks, air, and water. Sunlight is also a natural resource.
The major natural resources of Earth are:
- rocks
- minerals such as metals
- Fossil fuels such as coal found in rocks
- Soil
- Air
- Water
- Living things
- Sunlight
Man-Made resources
Resources made by humans are known as man-made resources.
The most important of these are:
- Foods, including pasta and bread
- Leather, from animal skins
- Natural fibers, cotton and linen from plants, wool from animals
- Plastics and synthetic fibers such as polyester made from oil
- Fuels like petrol, diesel, and kerosene, made from oil
- Metals, including iron and aluminum, made from minerals in rocks
- glass, made from minerals found in sand
- Ceramics such as bricks and porcelain made from clay
- Cement made from limestone, clay and other minerals found in rock
- Medicines, made from plants, animals and minerals
Renewable and non-renewable resources
• Resources that never run out or replenish faster than they are used are renewable resources. Eg. Timber in a forest.

• Resources that run out are non-renewable resources. Eg. oil

Living things as a resource
Living things such as plants and animals are resources too. Humans use plants and animals for food, shelter, building materials, clothing, medicines, fertilizers, fuel, and many other purposes.
Living things are a renewable resource because they reproduce. A forest can grow back after a few decades. Animals like cows are replaced through reproduction.
Air as a resource
Air is a mixture of gases and suspended particles such as dust, smoke, and water droplets.

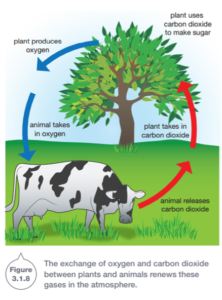
Air is a renewable resource
Oxygen in the air can be replenished through photosynthesis, which uses water and carbon dioxide. This oxygen is then used by living things. Oxygen cycles through the Earth’s atmosphere, soils, rocks, water, and organisms.
Sunlight is a resource
- Plants use sunlight to produce food.
- Sunlight warms the Earth’s atmosphere, land, and water, keeping it warm enough for most water to stay liquid. If Earth cooled too much, then all water would freeze, turning into ice. Living organisms contain water and so they would freeze too.
Rocks as a resource
Rocks provide two different resources:
- the rocks themselves
- minerals found in rocks
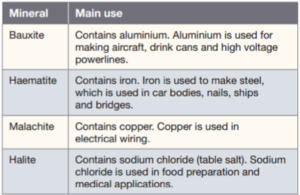
Rocks are made from substances called minerals. minerals differ in their physical properties such as color and hardness. Minerals have a variety of uses. Rocks are an nonrenewable resource.
Rocks are broken down (weathered) into smaller particles such as sand, silt, and clay. The small particles are carried away by the wind, water, and ice in a process called erosion. The particles are then dropped somewhere when the wind, water, or ice stops carrying them. When the particles drop, this is called deposition.
Soil is composed of:
- Fine rock particles (sediments)
- Living organisms
- Humus (decaying wastes and dead organisms)
- water
- dissolved minerals and gases
Soil: a Non-renewable resource
Soils are not being renewed at the same rate at which they are being used. Soil can blow away in the wind and wash away in floods. Soil often takes hundreds of thousands of years to form soil only a few centimeters thick.

Conserving resources
We must conserve our valuable resources, a number of ways this can be done are by doing the following:
- Limiting consumption: everyone should avoid wasting resources by only as much as needed.
- Increasing the price: making things more expensive deters people from overusing a resource. This works because people will not waste a resource if it costs them a lot of money.
- Using alternative resources: For example, electric cars save petrol which keeps oil for other vital uses such as making plastics.
- Public awareness campaigns: public awareness campaigns use the media to educate people about the need to conserve resources.
- Recycling: recycling is the process of reusing materials rather than throwing them away and then having to make more of the material. For example, re-using aluminum means that less bauxite needs to be mined.


