Liquid freezes to form frost on cold mornings. When it’s really cold, water can form ice and snow. As the temperature increases during the day, the frost, ice, and snow begin to melt to form pools of liquid water. Water can be changed from one state into another by adding energy to it or by removing energy from it. This is done by heating it up or cooling it down.
Adding Heat
A solid, liquid or gas might just increase its temperature when heated. However if you add enough heat, the substance will change its state. Given enough heat, solids will change into liquids and liquids will change into gases.

Melting
Melting is the process in which heat causes a solid to change into a liquid. Although the physical properties of the substance change, the substance itself is exactly the same as it was before. Ice (solid water) is exactly the same substance as the liquid water it melts into when it is heated. Likewise, the solid wax that makes up a candle is exactly the same substance as the clear, molten drips of wax that slide down its side.
Heat adds energy to the particles in a solid, making them vibrate faster. If you add enough heat, then the particles at the edges of the solid will be vibrating so violently that they will break free, allowing them to melt away from the others in the solid. You can see this in the melting butter here.

Melting point
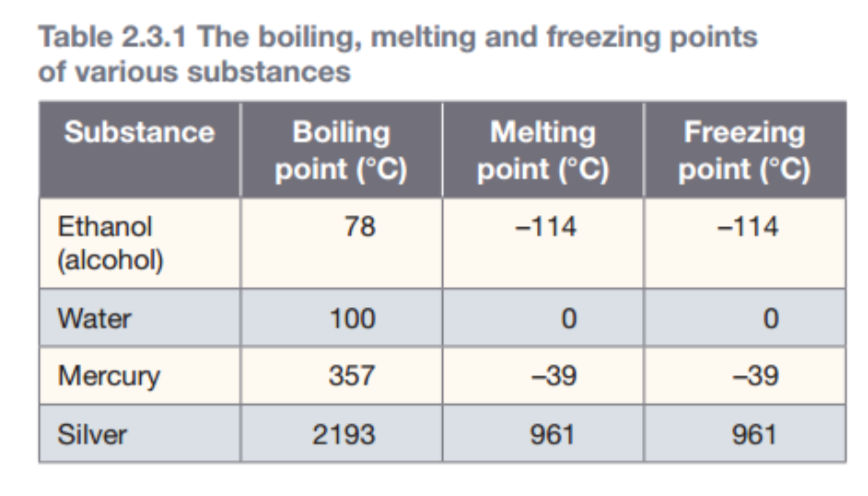
The temperature at which a solid melts is known as its melting point. A substance is solid below its melting point and is molten (a melted liquid) above it. For example, water, has a melting point of 0˚C.
Evaporation
Evaporation is the process in which heat causes a liquid to change into a gas. Evaporation is sometimes also known as vaporization.
For example, heat causes liquid water to evaporate (or vaporize), turning it into the gas known as water vapor.
Wet clothes eventually dry out because the liquid water in them has evaporated to become water vapor. This water vapor then escapes from the clothes and joins the other gases of the air.
Remember in solids and liquids the particles are stuck to each other by bonds.
If you add enough heat, and make the particles vibrate faster, you can get them to loosen. Keep adding heat and the bonds will loosen and the particles will vibrate so much that they break away and become gas particles.

Boiling
Boiling is a special case of evaporation. Evaporation occurs at any temperature, but boiling only happens at a temperature known as the boiling point. The boiling point of water is 100˚C, and when we heat up water like it a kettle it starts to turn into a gas, that’s why we can see bubbles forming.
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes from liquid into a gas.
For liquid water, the HIGHEST temperature it can be is 100˚C, before it turns into a gas. In the same way 100˚C is the LOWEST temperature that water vapor (water in its gaseous form) can be.
Sublimation

Identifying Boiling

Removing heat
The temperature of a substance drops when heat is removed from it. A substance might change state if sufficient heat is removed from it.
Freezing
Freezing (also known as solidification) occurs when heat is lost and a liquid changes into a solid.
An example of freezing is shown in the image below. These snowflakes show some of the amazing shapes that can form.
As a liquid cools, energy is lost from its particles and the particles move more slowly than before . If you remove enough energy, then the particles will end up just vibrating on the spot. Bonds form between the particles, locking them into their position to form a solid of definite shape and size.
The temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid, is known as the freezing point.
Condensation
Condensation occurs when a substance loses heat and changes from a gas into a liquid.
Your lungs are full of water vapor (gaseous water) that will condense into tiny droplets of liquid water when you breathe out onto something cold, like a window or mirror.
Likewise, water vapor in the air will condense on a cold night to form droplets of liquid dew that will make the lawn and spider webs wet.

As a gas is cooled, its particles slow down. When they have slowed enough, the individual particles begin to attract each other and form bonds that will tie their movement to the other particles in the substance. They now act as a group, forming droplets of liquid.
Steam is water vapour that has condensed to form a cloud of tiny but visible liquid water droplets in the air. Water vapor emerges as a gas from a kettle or from a boiling pot on the stove but quickly cools in the air to form a visible fog of tiny liquid water droplets.
2.3 UNIT REVIEW

Answers:
- a) 100˚C
b) 0˚C
2)$CO2$
- a) vaporisation
b) solidification
- a) condensation
b) freezing
c) melting
d) evaporation
-
The melting and freezing point of a substance are the exact same because, the melting point of the substance is the highest temperature that is can exist as a solid and the freezing point is the lowest temperature it can exist as a liquid.
-
The signs that show water is boiling include large bubbles forming instead of small bubbles when water is being heated up. The small bubbles forming are gases in the water evaporating and the large bubbles are water evaporating.
-
The reason why water evaporates despite the temperature never getting to the boiling point is because the water particles on the surface of the clothes absorb enough energy to break their bonds with other water particles and turn into a gas.
-
a)

