Acids have a reputation for being extremely dangerous. But some, like those found in lemon juice and vinegar, are safe enough to eat and use in cooking. Bases also vary, from the caustic soda used to strip paint to gentler bases found in soap and disinfectant. Indicators show whether a solution is acidic or basic (alkaline). Some also measure how acidic or alkaline the solution is.
Acids
An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions (H+) into an aqueous solution. Eg. hydrochloric acid HCl.

Properties of acids
Acids have similar chemical properties. Acids:
- Are corrosive
- have a sour taste
- turn blue litmus paper red
- react with some metals, releasing hydrogen gas and leaving the salt behind.
- conduct electricity
- are neutralized by bases, producing water and a salt

Acids are molecular compounds made up of atoms from different elements. For example, a molecule of nitric acid ($HNO_3$) contains one hydrogen atom, one nitrogen atom, and three oxygen atoms. Like nitric acid, all acids have hydrogen atoms in their molecules.
The acids you will work within the laboratory are not pure substances but are solutions of acid mixed with water. When mixed with water, some of the hydrogen atoms in the acid molecule are released to form hydrogen ions (H+).
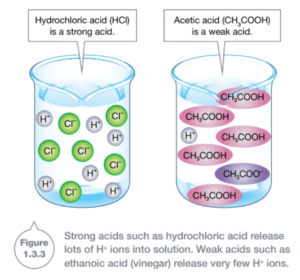
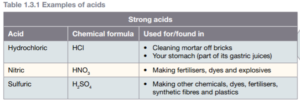
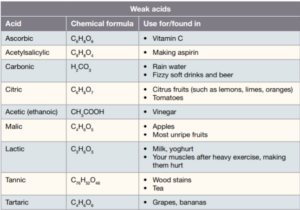
The strength of an acid depends on how many hydrogen ions are released. An acid is strong if most of its molecules release hydrogen ions into the solution. Nitric acid is an example of a strong acid, as are hydrochloric acid (HCl). An example of a weak acid is vinegar (ethanoic acid or acetic acid).
Bases and alkalis
Ions are not always single charged atoms’ like the hydrogen ions (H+) that acids release. Ions can also be charged groups of atoms.
This type of ion is known as a polyatomic ion (poly means more than one). An example is the hydroxide ion (OH-).
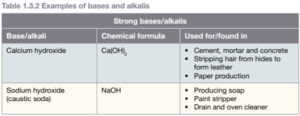
A base is a substance that releases hydroxide ions (OH-). You use a weak base every time you use soap. If a base can be dissolved in water it is also known alkali. The solution it forms is known as an alkaline solution. Bases such as caustic soda can burn you as badly as acids can, and so bases need to be treated with as much care acids. All bases have similar chemical properties. Bases:
-
are caustic
-
have a soapy, slimy feel
-
turn red litmus paper blue
-
have a bitter taste
-
conduct electricity
-
are neutralized by acids, producing water and a salt


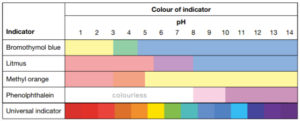
pH
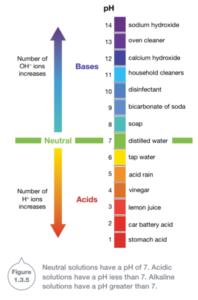
The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution is measured using the pH scale. In an acidic solution, there are more hydrogen ions than hydroxide (OH-). In contrast, an alkaline solution has more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions.
Pure water is neither an acid nor a base. It is neutral having equal numbers of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. It has a pH of 7.
Measuring pH
indicators are chemicals that change color to show whether a substance is acidic, neutral, or basic. A common indicator is litmus paper, which turns red when dipped into acids and blue when dipped into a base. While litmus doesn’t tell you what the pH of a solution is, other indicators such as universal indicators do.